
THE COSMOS AND MANKIND
(from Anaximander to Michel Mayor*)
*From the father of scientific thought to the co-discoverer of the first extrasolar planet.

ANTIQUITY
-
Anaximander of Miletus (c. 610-546 BC [1]): … Conceived the first mechanical model of the World, in which the Earth floats in equilibrium, motionless at the center of everything, unsupported by anything. Its shape is that of a cylinder whose height is one-third of its diameter. The flat upper surface forms the habitable world surrounded by oceans… Observed that the sky seems to rotate around the North Star… May have discovered the obliquity of the ecliptic…
* -
Anaximenes (c. 585-525 BC): … Understood that the light of the Moon is borrowed from the Sun…
* -
Pythagoras of Samos (c. 569-495 BC [2]): … Proposed that the Earth is spherical in shape… First to call the sky ‘cosmos’ (order)… May have been the first to observe the obliquity of the ecliptic [3]…
* -
Parmenide of Elea (late 6ᵗʰ century – mid-5tᵗʰ century BC): … Claimed that the Earth is spherical and at the center of the Universe…
* -
Philolaus of Croton (c. 470-390 BC): … Measured the lunar month at 29 and a half days, the lunar year at 354 days, and the solar year at 365 days… First thinker to consider that the Earth is not stationary at the center of the Universe. For the first time, Earth was considered a planet, but its orbit was not heliocentric: it was thought to revolve once a day around a ‘central fire’ whose light was reflected by the Sun…
* -
Meton of Athens (second half of the 5ᵗʰ century BC): … With Euctemon, carried out a series of solstice observations to determine the length of the tropical year… Studied the Moon’s phases and stated there are exactly 235 lunations in 19 years (Metonic cycle)…
* -
Eudoxus of Cnidus (c. 408–355 BC): … Formulated a theory on the motion of the planets…
* -
Heraclides Ponticus (c. 388-310 BC): … Hypothesized that the Earth rotates on its axis to explain the apparent movement of the stars in the night sky… Put forward a geocentric system in which Venus and Mercury revolve around the Sun…
* -
Aristotle (384-322 BC): … Provided some of the first observational evidence for a spherical Earth, such as the rounded shape of its shadow on the Moon during eclipses [4]… Author of the earliest known estimate of Earth’s circumference [5]…
* -
Pytheas of Massalia (c. 380-310 BC): … Calculated with great precision the obliquity of the ecliptic…
* -
Gan De (4ᵗʰ century BC): … Together with Shi Shen, the first historically attested to compile a star catalog (preceded only by anonymous Babylonian lists)… Made one of the earliest detailed observations of Jupiter and reported the existence of a small reddish star near it [6]… Calculated with great precision the sidereal period of Jupiter and the synodic periods of Mercury and Venus…
* -
Shi Shen (4ᵗʰ century BC): … Compiled a catalog of 121 stars in the Shi's Treatise on Stars… Gave instructions for predicting eclipses based on the position of the Moon relative to the Sun… Observed sunspots [7]…
* -
Autolycus of Pitane (c. 360-290 BC): … Produced two of the oldest surviving treatises on astronomy: On the Moving Sphere and On Risings and Settings…
* -
Epicurus (c. 341-270 BC): … Supported the theory of a plurality of Worlds: ‘[…] not only is the number of atoms infinite, but so is the number of Worlds in the Universe. There are an infinite number of Worlds like ours and an infinite number of Worlds different from ours’…
* -
Timocharis of Alexandria (c. 320-260 BC): … With Aristyllus of Samos (c. 4ᵗʰ century BC – 280 BC), created the very first star catalog in the Western world…
* -
Aristarchus of Samos (c. 310-230 BC): … Hypothesized that the Earth rotates on its axis and orbits the stationary Sun… Attempted to measure the diameters of the Sun and Moon… Estimated the Earth-Sun distance [8] compared to the Earth-Moon distance [9]…
* -
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (c. 276-194 BC): … Calculated the Earth’s circumference to within a few hundred kilometers [10]… Developed eclipse tables and an astronomical catalog of 675 stars… Demonstrated and measured the inclination of the ecliptic…
* -
Hipparchus of Nicaea (c. 190-120 BC): … Established accurate quantitative models of the Sun and Moon’s motions… Determined the Earth-Moon distance with good precision [11] by studying lunar eclipses… Compiled a star catalog and discovered the precession of the equinoxes… Invented the astrolabe…
* -
Zhang Heng (78-139): … Invented the first hydraulically driven armillary sphere… Produced an extensive catalog of about 2,500 stars…
* -
Ptolemy (c. 100-168): … Wrote the Almagest, the only complete ancient work on astronomy to survive… Author of a geocentric system: the stars attached to the outermost celestial sphere mark the end of the Universe; the Earth is fixed at the center, with the Moon, Sun, and planets orbiting around it…
MIDDLE AGES -
Al-Khwârizmî (c. 780-850): … Published, under Caliph Al-Ma’mun, a ‘zij’ (set of tables) for calculating and predicting the positions of celestial bodies at a given date [12]…
* -
Al-Maʾmūn (786-833): … Founded, in 829, the Baghdad Observatory, the first permanent observatory in the world…
* -
Al-Farghani (9ᵗʰ century – c. 861): … Between 833 and 857, wrote Kitab fi Jawani [13] (‘Compendium on the Science of the Stars’ or ‘Elements of Astronomy in some translations’)… Authored two other works on sundials and the astrolabe… Proposed new values for the obliquity of the ecliptic, the precession of the Sun and Moon’s apogees, and the circumference of the Earth…
* -
Al-Battani (c. 858-929): … Corrected some of Ptolemy’s calculations and produced new tables for the Sun and Moon… Discovered the motion of the Sun’s apogee, calculated the precession of the equinoxes (54.5″ per year), and the tilt of Earth’s axis (23° 35′)… Showed that the Earth-Sun distance varies during the year… Compiled a catalog of 489 stars… Refined the length of the year to 365 days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, and 24 seconds…
* -
Abd al-Rahman al-Soufi (903-986): … Improved Ptolemy’s star catalog… First to mention the Large Magellanic Cloud (‘the white ox’ [14])… Possibly the first to report the Andromeda Galaxy (M31)… First to correlate Greek and Arabic star names… Calculated with relative precision the length of the tropical year… Found many innovative uses for the astrolabe…
* -
Alhazen (c. 965-1040): … Discovered that twilight is caused by refraction of sunlight in the atmosphere… Demonstrated that the Moon’s light comes from the Sun [15]… Hypothesized that a moving object continues in motion until acted upon…
* -
Anonymous Chinese (11ᵗʰ century): … Observed the Crab supernova from its explosion on July 4, 1054, and for about two years [16]…
* -
Shen Kuo (1031-1095): … Observed a 3° shift in the North Star’s position compared to Zu Geng’s records 600 years earlier… Determined with great accuracy the coordinates of planetary and lunar motions by making observations three times a night for five years [17]… Hypothesized that celestial bodies were spherical…
* -
Omar Khayyam (c. 1048-1131): … Constructed astronomical tables known as Zij-e Malikshahi… Introduced a leap year system similar to the Julian calendar… Fixed the solar year at 365.24219858156 days…
MODERN ERA -
Nicolaus Copernicus (1473-1543): … Wrote the major work De revolutionibus orbium coelestium (‘On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres’) [18] qui offre une vision de l’Univers alternative (à celle proposée jusque-là par le géocentrisme) avec le Soleil au centre de l’Univers…
* -
Tycho Brahe (1546-1601): … Built instruments allowing unprecedented precision… Made continuous observations of the Sun, Moon, planets, and stars for 30 years, correcting errors in existing ephemerides… Observed the supernova of 1572, challenging Aristotle’s immutability of the heavens… Observed a comet in 1577 whose orbit crossed the planets’ paths, further disproving Aristotelian theories…
* -
Giordano Bruno (1548-1600): … Developed the theory of heliocentrism and argued for an infinite universe with countless Worlds [19]…
* -
Galileo Galilei (1564-1642): … Improved the telescope… Discovered Jupiter’s four largest moons (Io, Europa, Ganymede, Callisto)… Defended the Copernican model and heliocentrism [20], along with satellite motion… Observed mountains on the Moon [21]…
* -
Johannes Kepler (1571-1630): … Discovered that planets move in elliptical orbits… Invented the high-magnification, wide-field telescope, improving Galileo’s optics…
* -
Giovanni Domenico Cassini (1625-1712): … Founded the Paris Observatory… Discovered four moons of Saturn and the main division in its rings… Measured the rotation periods of Mars and Jupiter… Mapped the Moon in detail…
* -
Christian Huygens (1629-1695): … Discovered Titan, Saturn’s largest moon… Provided the first fairly complete description of the Solar System with six planets and six moons, giving an unprecedented idea of its scale…
* -
Isaac Newton (1643-1727): … Formulated the laws of universal gravitation and motion [22]… Studied light refraction, showed white light splits into a spectrum… Invented the reflecting telescope…
* -
Ole Christensen Rømer (1644-1710): … Estimated the speed of light [23] by observing eclipses of Io, Jupiter’s innermost moon…
* -
Edmond Halley (1656-1742): … Charted the southern sky… Determined the periodicity of the comet of 1682 (Halley’s Comet) at about 76 years [24]… Helped publish Newton’s ‘Principia’… Measured the Earth-Sun distance during a Venus transit…
* -
John Michell (1724-1793): … Proposed the idea of an object so massive that light could not escape (black holes)…
* -
Charles Messier (1730-1817): … Discovered the Dumbbell Nebula (M27) in 1754, the Whirlpool Galaxy (M51) in 1773, and the Virgo A Galaxy (M87) in 1781… Famous for creating the Messier Catalog of over 100 deep-sky objects [25]…
* -
William Herschel (1738-1822): … Discovered Uranus (1781) and two of its satellites (1787) as well as two satellites of Saturn (1789)… Demonstrated and calculated the speed at which our Solar System moves… [26]… Discovered double stars and showed that they orbit around their common center of gravity… Discovered infrared light…
* -
Anders Lexell (1740-1784): … Deduced the existence of Neptune from the disturbed motions of Uranus, whose orbit he had calculated…
* -
Giuseppe Piazzi (1746-1826): … Discovered Ceres in 1801, the smallest known dwarf planet in the Solar System [27]…
* -
Pierre-Simon de Laplace (1749-1827): … Wrote the Treatise on Celestial Mechanics [28] (1799-1825)… In 1796, proposed his theory of the formation of the Solar System: born from the condensation of a vast nebula composed of gas and dust…
* -
John Goodricke (1764-1786): … Demonstrated that the brightness of the star Algol (Beta Persei) varied periodically…
CONTEMPORARY ERA -
Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel (1784-1846): … Performed in 1838 the first precise measurements of the distance to a nearby star [29] using a heliometer, applying the method known as parallax. This calculation made it possible to confirm the theory of heliocentrism [30]… Determined the masses of Jupiter and Saturn by observing the motion of their satellites… Measured the diameter of the Sun…
* -
Joseph von Fraunhofer (1787-1826): … Invented the spectroscope… Discovered that the spectrum of the Sun contained dark lines… Is the father of the so-called ‘equatorial’ telescope mount…
* -
Heinrich Schwabe (1789-1875): … Discovered the periodicity (cycle) of sunspots…
* -
John Herschel (1792-1871): … Discovered thousands of double stars, star clusters, and nebulae… Invented astronomical instruments…
* -
Christian Doppler (1803-1853): … Discovered that when a luminous body approaches or recedes from the observer, the wavelength of light decreases or increases (Doppler effect). This discovery made it possible to determine the velocities of distant objects…
* -
Urbain Le Verrier (1811-1877): … Discovered the existence of Neptune, calculating its characteristics and position by observing the perturbed orbit of Uranus…
* -
Johann Gottfried Galle (1812-1910): … Discovered the existence of Neptune, having calculated its characteristics and position by observing the perturbed orbit of Uranus…
* -
Léon Foucault (1819-1848): … Demonstrated the rotation of the Earth around its axis (Foucault pendulum)… Determined the speed of light as 298,000 km/s (rotating mirror experiment)…
* -
Hippolyte Fizeau (1819-1896): … Captured in 1845 the first clear photograph of the Sun… Discovered in 1848 the frequency shift of a wave when the source and receiver move relative to each other (Doppler–Fizeau effect). This led him to predict the redshift of light waves…
* -
William Huggins (1824-1910): … Demonstrated in 1863 that stars are composed of the same elements found on Earth and at the surface of the Sun… First to distinguish nebulae from galaxies by showing that some, such as the Orion Nebula, display the spectrum of a hot gas, while others, like the Andromeda Galaxy, show a spectrum characteristic of a star… Began using spectral analysis to study the chemical composition of stars…
* -
Asaph Hall (1829-1907): … Discovered in 1877 the moons of Mars (Phobos and Deimos)…
* -
James Clerk Maxwell (1831-1879): … Unified electricity, magnetism, and induction into a single set of equations… Interpreted light as an electromagnetic phenomenon based on Michael Faraday’s work… Demonstrated that electric and magnetic fields propagate through space at the speed of light in the form of a wave…
* -
Camille Flammarion (1842-1925): … Founded the French Astronomical Society… Father of popular science, his major work Astronomie populaire was the first scientific book aimed at the general public…
* -
Wilhelm Röntgen (1845-1923): … Discovered in 1895 X-rays (so named due to the lack of an appropriate term) by studying the fluorescent light emitted when an electric current passed through a low-pressure gas tube…
* -
Konstantin Tsiolkovski (1857-1935): … Considered the father of modern astronautics… Demonstrated the effectiveness of liquid propellants and multi-stage rockets…
* -
Max Planck (1858-1947): … Was one of the founders of quantum mechanics… Discovered the spectral law of blackbody radiation…
* -
Annie Jump Cannon (1863-1943): … Catalogued some 250,000 stars, thousands of stellar spectra, and helped establish the link between a star’s color and the elements in its atmosphere… Is the mother of the current stellar classification system (see Harvard classification)…
* -
Antonia Maury (1866-1952): … Observed that some stars of the same color could have different luminosities… Her classification of stars had a major influence on the work that led to the development of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram…
* -
Henrietta Swan Leavitt (1868-1921): … Discovered a relationship between the luminosity of certain variable stars (Cepheids) and their period of variation: the slower they vary, the intrinsically brighter they are. This discovery made it possible to calculate precise distances on an intergalactic scale…
* -
Ejnar Hertzsprung (1873-1967): … First to propose an absolute measure of stellar brightness—the absolute magnitude—defined as the apparent magnitude a star would have if observed from a distance of 10 parsecs [31]… Developed, together with [32] Henry Norris-Russell (1877–1957), the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram, a chart illustrating the relationship between stellar luminosity and temperature, allowing the identification of different categories of stars, such as red giants and white dwarfs…
* -
Vesto Slipher (1875-1969): … Discovered, by observing their spectral lines, the redshift of galaxies, thus noting that—unlike the Andromeda Galaxy—most are moving away from us…
* -
Albert Einstein (1879-1955): … Developed the theory of special relativity (light has the same speed in all inertial frames; absolute time and durations do not exist across the Universe; each observer has their own measurement of time and length)… Developed the theory of general relativity (generalizing relativity to non-inertial frames; gravity is no longer a force, masses determine the geometric properties of spacetime)… Predicted the existence of black holes [33] and gravitational waves…
* -
Arthur Eddington (1882-1944): … Identified the limit that bears his name, corresponding to the maximum luminosity a star of a given mass can have without beginning to lose the outer layers of its atmosphere… Correctly suggested that nuclear fusion could be the primary source of energy in stars…
* -
Alexandre Friedmann (1888-1925): … A découvert que les équations d’Einstein permettent la description d’un univers en évolution et a introduit pour la première fois l’idée d’un univers en expansion… Est considéré comme l’un des pères fondateurs de la théorie du Big Bang…
* -
Edwin Hubble (1889-1953): … Demonstrated, through the observation of Cepheid variable stars [34], that the spiral nebula of Andromeda lies far beyond the limits of our own galaxy, thereby measuring for the first time the distance to what was revealed to be the Andromeda Galaxy… Proved the existence of other galaxies beyond the Milky Way—by observing a redshift in the spectra of several, he showed that they are moving away from each other at a speed proportional to their distance [35]… Established a galaxy classification system, which today bears his name (see Hubble sequence)…
* -
Georges Lemaître (1894-1966): … His ‘primordial atom theory’, aimed at explaining the origin of the Universe, laid the foundation for the Big Bang theory… First to establish the constant relationship between distance and recession velocity of galaxies, and to deduce that the Universe is expanding…
* -
Fritz Zwicky (1898-1974): … Introduced, with German astronomer Walter Baade, the term ‘supernova’ and suggested that these events can create neutron stars that emit cosmic rays… Discovered 120 supernovae… Proposed, in 1933, the existence of invisible matter between galaxies (dark matter)…
* -
Jan Oort (1900-1992): … Demonstrated, in 1927, that the stars and gas clouds in our galaxy rotate around a central point… Revealed the spiral structure of the Milky Way… Developed, from 1950, the theory—now universally accepted—that there exists a vast concentration of comets (Oort Cloud) at distances from the Sun between 40,000 and 100,000 astronomical units… Showed, in 1951 (simultaneously with a team of American astronomers), that hydrogen, the most abundant element in the Universe, can be detected by radio at a wavelength of 21 centimeters… Calculated the distance from the Sun to the galactic center…
* -
Cecilia Payne-Gaposhkin (1900-1979): … Was, in 1925, one of the first astronomers to suggest that stars are composed mostly of hydrogen, contrary to the scientific consensus of the time… Discovered that the OBAFGKM classification actually indicates the temperature of stars…
* -
George Gamow (1904-1968): … A publié un article capital sur la formation des éléments au cours des premières phases d’expansion de l’Univers, participant ainsi à l’élaboration de la théorie du Big Bang…
* -
Karl Jansky (1905-1950): … Discovered, in 1932, that our Galaxy emitted radio waves [this event marks the birth of radio astronomy]…
* -
Gérard Kuiper (1905-1973): ... Proposed the existence of an asteroid belt beyond Neptune’s orbit (Kuiper Belt)… Discovered two moons in the solar system: Miranda, a moon of Uranus (1948), and Nereid, a moon of Neptune (1949)… Detected, in 1944, the presence of methane in Titan’s atmosphere and, in 1947, carbon dioxide in Mars’ atmosphere…
* -
Clyde William Tombaugh (1906-1997): ... Discovered, in 1930, the dwarf planet Pluto…
* -
Hans Bethe (1906-2005): ... Contributed to the understanding of stellar nucleosynthesis through his work with Carl von Weizsäcker and Charles Critchfield, notably studying the various fusion reactions occurring in pulsar stars (1938)… Hypothesized that the energy produced in stars comes from thermonuclear fusion reactions in which hydrogen is converted into helium…
* -
Sergueï Korolev (1907-1966): … Was the designer of the first Soviet space program…
* -
Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1910-1995): … Demonstrated that a star’s end of life depends on its mass… Determined the threshold beyond which a white dwarf becomes unstable under certain conditions and collapses into a neutron star, initiating the supernova process (this limit is now known as the Chandrasekhar limit [36].)…
* -
Sir Bernard Lovell (1913-2012): … Played a decisive role in the construction of the world’s first large radio telescope [37]… Achieved the first radio detection of meteors…
* -
Audouin Dollfus (1924-2010): … Discovered Janus, a moon of Saturn… Determined the composition of the Martian soil… Detected an atmospheric remnant on Mercury… Selected the landing site for the Apollo XI mission…
* -
Anthony Hewish (1924-2021): … Played a decisive role in the discovery of pulsars [38] by his student Jocelyn Bell in 1967, while he was her thesis supervisor…
* -
Allan Sandage (1926-2010): … Discovered, with Thomas Matthews in 1960, the first quasar (3C 48)…
* -
George Abell (1927-1983): … Produced the first detailed survey of galaxy clusters…
* -
Vera Rubin (1928-2016): … Observed that the stars on the outskirts of the Andromeda Galaxy move much faster than they should if gravity were produced only by visible matter… She is today regarded as the discoverer of dark matter…
* -
Neil Armstrong (1930-2012): … Was the first man to walk on the Moon…
* -
Yuri Gagarin (1934-1968): … Was the first man to make a flight into space [39]…
* -
Carl Sagan (1934-1996): … Created the popular science documentary series Cosmos, broadcast on television across several continents… Designed the plaques and golden records carried by the Pioneer and Voyager probes… Predicted the existence of methane lakes on Titan… Was one of the founders of exobiology…
* -
Kip Thorne (1940-): … Played a decisive role, together with Rainer Weiss and Barry C. Barish, in the discovery of gravitational waves [40]…
* -
Stephen Hawking (1942-2018): … Predicted in 1974 that radiation should escape from the event horizon of a black hole (Hawking radiation)…
* -
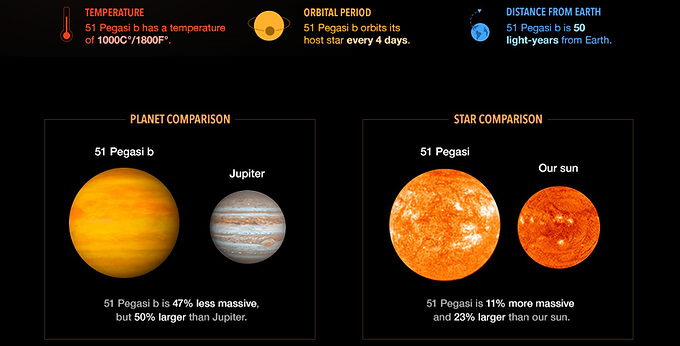
Michel Mayor (1942-): … In 1995, together with Didier Queloz, discovered the first exoplanet orbiting a Sun-like star [41], 51 Pegasi b (also called ‘Dimidium’) [42]…
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*

© NASA / JPL-Caltec
The 51 Pegasi system is located 51 light years from Earth.
[1] The first Olympic Games are reputed to have taken place in 776 BC on the site of Olympia* (Peloponnese, Greece). This date marks the beginning of the Olympic calendar, where years are grouped into Olympiads. According to Diogenes Laërtius (2ᵈ–3ʳᵈ c. AD, Lives, Doctrines and Sayings of Illustrious Philosophers, II, 1), who refers to Apollodorus of Athens (Chronicle*, 2ᵈ c. BC), Anaximander was (had?) 64 years old in the second year of the 58ᵗʰ Olympiad, and he is said to have died shortly thereafter. Since the Games had been held every 4 years from their creation in July*** 776 BC, the second year of the 58ᵗʰ Olympiad [Ol. 58,2] would correspond to the period from July 547 to July 546 BC****. From these data, one can deduce that Anaximander was born between July 611 and July 610 BC*****. *Information based on inscriptions found at Olympia, listing the winners of a footrace organized every four years starting from 776 BC. **A (lost) chronography of Greece from the year 1184 (fall of Troy) to the year 144 BC. ***The beginning of these first Games is traditionally fixed at July 1 in the Gregorian calendar; we only know that they began at the first or second full moon following the summer solstice (June 20 or 21). ****One adds 57 Olympiads to the first having taken place in 776 BC, then adds 1 year: -776 + (57×4) + 1 = -547. *****If one wishes to risk narrowing further the range regarding the date of Anaximander’s birth, one may cross the information given in Refutation of All Heresies (I, 5, 3ʳᵈ c. AD), attributed to Hippolytus of Rome (attribution contested), that he was born in the third year of the 42ᵈ Olympiad, with that advanced by Apollodorus of Athens which led us to estimate that the Milesian philosopher was born between July 611 and July 610 BC. The first piece of information leads us to find 610 BC as the beginning of the one-year period in which Anaximander could have been born: -776 + (41×4) + 2 = -610. The third year of the 42ᵈ Olympiad extending over the period from July 610 to July 609 BC, one must, in order to attempt to reconcile the two assertions (that of Apollodorus and that of Hippolytus), suppose that Anaximander was born around July 610 BC. A solution not to contradict either Apollodorus or Hippolytus is to make the 42ᵈ Olympiad begin at the very beginning of the month of July—say July 1—and the 58th Olympiad later in the month—say July 15: thus, it would suffice to make Anaximander be born between these two dates, for example on July 7 (610 BC), so that he was indeed born during the third year of the 42ᵈ Olympiad and that he was 64 years old (610–546=64) in the course of the second year of the 58ᵗʰ Olympiad. [2] In The Voyages of Anaximander, the year 569 BC was chosen for the birth of Pythagoras. However, there are many uncertainties regarding the year of birth of the Samian philosopher: born in 540 BC according to Jean-Baptiste J. Delambre*, he is said to have been born around 570 BC if we follow Aristoxenus of Tarentum (4ᵗʰ c. BC); in 569 or 606 BC according to calculations by Eratosthenes (3ʳᵈ–2ᵈ c. BC) reported by Diogenes Laërtius; in 580 BC according to Porphyry of Tyre (3ʳᵈ–4ᵗʰ c. AD); in 590 BC, it would seem, according to Iamblichus (3ʳᵈ–4ᵗʰ c. AD); etc. Finally, Paul Tannery**, who synthesized the opinions of various doxographers, philosophers, and historians, estimated that Pythagoras would have lived ‘between 572 and 482’ BC. *Histoire de l’astronomie ancienne, Book I, Chapter I, 1817, p. 15. **Pour l’histoire de la science hellène, chap. II: La Chronologie des « Physiologues », 7. – Anaximandre et Pythagore, 1887, pp. 45–46. [3] Some attribute this discovery to Anaximander, others to Pythagoras. [4] Lunar eclipses are proof of the sphericity of the Earth, for the shadow cast by the Earth on the Moon is round, and only a sphere can, regardless of the alignment of the celestial bodies, cast a shadow of this shape. [5] He estimated the circumference of the Earth at 400,000 stadia (≈60,000 km). Today it is measured at 40,075.02 km at the equator. [6] The astronomer and historian Xi Zezong maintains that this would have been a naked-eye observation of Ganymede (Jupiter III Ganymede) made during the summer of 365 BC (or 362 BC), well before its (re)discovery by Galileo in 1610. [7] He supposed that these spots were eclipses that began at the center of the Sun and spread outward. [8] Surviving work: On the Dimensions and Distances [of the Sun and the Moon]. [9] He estimated the Earth–Sun distance at 18 or 20 times the Earth–Moon distance, instead of about 400 times in reality. [10] He compared the shadow of two objects located in two places, Syene (today Aswan) and Alexandria, considered to be on the same meridian, on June 21 (summer solstice) at local solar noon, and deduced the circumference of the Earth in a purely geometric way, obtaining a result very close to reality. [11] He placed the Earth–Moon distance within a ‘range’ of 62 to 77 Earth radii (60.2 in reality). [12] These astronomical tables are a compilation of Indian and Greek sources. [13] This book enjoyed wide circulation in the Muslim world. It was primarily an abridgment of Ptolemy’s cosmography, presenting it for the first time in a more descriptive than mathematical manner; however, it also corrected the Almagest by relying on the observations of other Persian astronomers. [14] The Book of Fixed Stars, published in 964. [15] In his book Shukūk ʿalā Baṭlamyūs, he also addressed the attraction of masses so accurately that some contemporaries believed he had an intuition of the principle of gravitational acceleration. [16] The event was reported by six accounts. The earliest dates to about a century after the appearance of the star. [17] Although star charts had been created in the meantime, this amount of astronomical observations collected over such a long period was matched in Europe only in the time of the astronomer Tycho Brahe (1546–1601). [18] The book was printed for the first time in 1543 in Nuremberg. [19] Giordano Bruno came into conflict with the Inquisition and was burned alive. [20] Galileo was condemned in 1633 for this reason by the Roman Catholic Church and was placed under house arrest for the remainder of his life. [21] ESPACE DES SCIENCES. How Galileo calculated the height of the mountains on the Moon (espace-sciences.org) [22] In one of the most important scientific books ever published: Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica. [23] In 1676, he estimated the speed of light at 220,000 km/s (its value, known today with precision, is 299,792.458 km/s). [24] Upon the return of this comet in 1758, it was named after him. [25] These objects are identified by the letter ‘M’ followed by their number in the catalog. [26] In 1783, he discovered that the Sun has a proper motion and that it carries its entire retinue of planets toward a point located in the constellation Hercules: the Apex. [27] Ceres is the largest and most massive object in the asteroid belt located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. [28] This major work, in five volumes, transformed Newton’s geometric approach to mechanics into an approach based on mathematical analysis. [29] The circumpolar binary star 61 Cygni, whose distance from the Earth was estimated at 10.9 light-years. [30] By observing the apparent motion of a star relatively close to the Earth over a period of 18 months, he noticed that this star traced a small ellipse on the celestial sphere. He explained this phenomenon by the motion of the Earth around the Sun. According to the principle of parallax, the dimensions of the ellipses are smaller the more distant the stars are. [31] 32.6 light-years. [32] The work of the two astronomers was developed independently. Although Hertzsprung’s work was published first, it appeared in an obscure German journal and remained unnoticed until 1913, the year when the American Russell published his own research. [33] The term ‘black hole’ was coined by the American physicist John Wheeler in 1967. [34] A Cepheid is a giant variable star that pulsates at a very regular rhythm. [35] This relationship, known as ‘Hubble’s law’, had, however, been predicted earlier by Georges Lemaître. [36] Equal to 1.4 times the mass of the Sun, this limit indicates the maximum mass that a star, having exhausted its thermonuclear fuel and become a white dwarf, can reach without becoming a neutron star or collapsing into a black hole. [37] The 76-meter antenna at Jodrell Bank in England. [38] These are thought to be neutron stars spinning very rapidly on their axes and emitting strong electromagnetic radiation along the direction of their magnetic axis. [39] During the Vostok 1 mission, on April 12, 1961, as part of the Soviet space program. [40] Kip Thorne is the co-founder of the LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory) project, which made this discovery possible. [41] The first exoplanet ever discovered is actually PSR B1257+12 b in 1992, orbiting a pulsar. [42] The announcement was made on October 6, 1995, at a conference held in Florence, Italy.
